Social Security is an essential government program that provides financial support to retirees, disabled individuals, and their families. For most working Americans, Social Security retirement benefits represent a significant portion of their post-retirement income. Deciding when to start collecting these benefits is a crucial financial decision that can have a lasting impact on one’s financial well-being during retirement. In this blog post, we will explore the factors to consider when determining the optimal time to begin receiving Social Security retirement benefits.
Understanding Social Security Retirement Benefits:
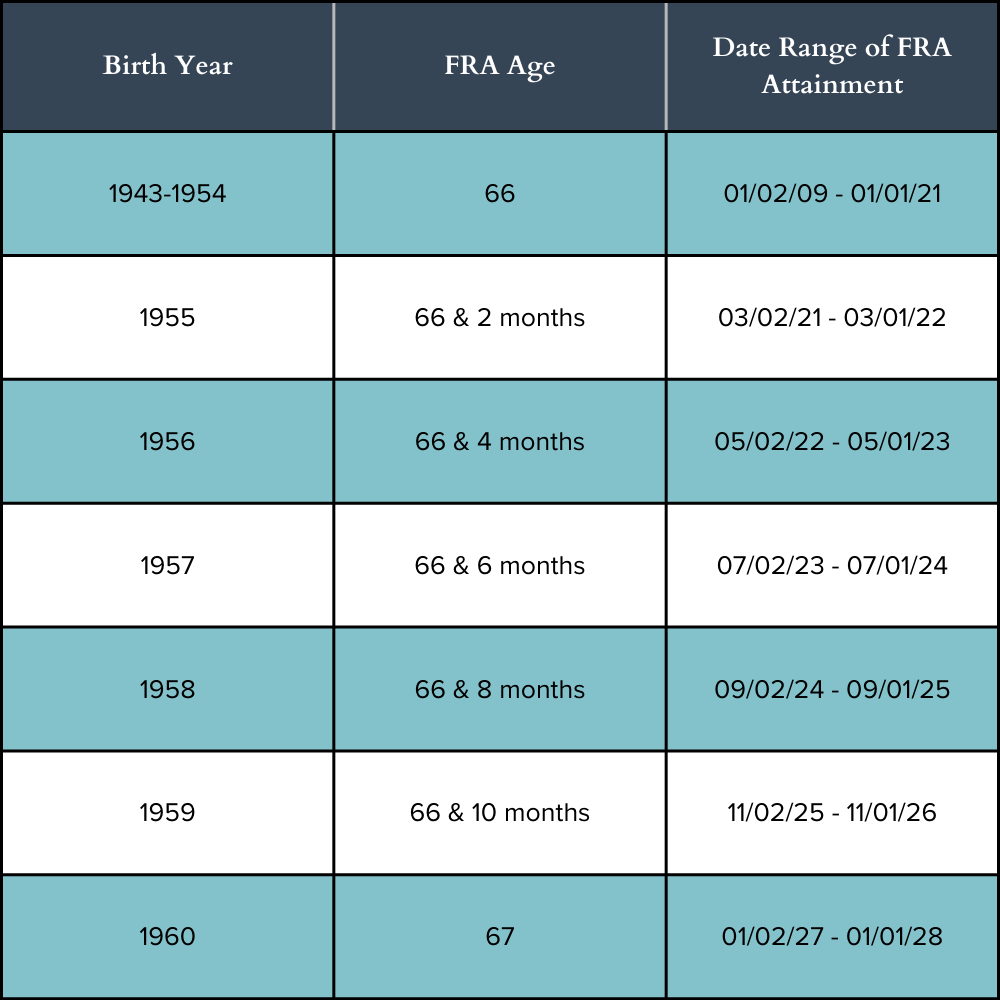
Before delving into when to start collecting Social Security benefits, it’s essential to understand how these benefits work. Social Security retirement benefits are based on your lifetime earnings, specifically your highest-earning 35 years of work. The age at which you can begin collecting full retirement benefits (“full retirement age,” or FRA) varies depending on when you were born.
Early Retirement: You can start receiving reduced benefits as early as age 62. However, if you choose to collect benefits before reaching your full retirement age, the amount you receive each month will be permanently reduced.
Full Retirement Age (FRA): Your full retirement age is based on your birth year and ranges from 65 to 67. If you begin collecting benefits at your FRA, you will receive your full entitled amount without any reductions.
Delayed Retirement: If you delay claiming benefits beyond your full retirement age, your benefits will increase by a certain percentage, known as delayed retirement credits. This increase continues until you reach the maximum age of 70. For persons born in 1943 or later, the delayed retirement credit adds an additional 8% per year to your benefit for each year you wait.
Factors to Consider:
Financial Need: One of the most critical factors in determining when to start collecting Social Security benefits is your financial situation. If you are facing financial hardships or need the income to cover essential living expenses, claiming benefits early might be necessary. However, remember that starting early will permanently reduce your benefit amount.
Health and Longevity: Consider your health and family history of longevity. If you expect to live a longer life, delaying Social Security benefits may be more beneficial in the long run, as it will result in higher monthly payments. A break-even analysis can help you determine the point at which you would receive the same total amount of Social Security benefits, regardless of whether you start early or delay. The break-even age typically falls somewhere in your 80s. If you expect to live beyond your break-even age, delaying benefits may be a more financially sound decision.
Other Sources of Income: Evaluate your other sources of retirement income, such as pensions, 401(k)s, IRAs, or other investments. If you have sufficient income from these sources, delaying Social Security benefits could allow you to maximize your overall retirement income.
Employment Status: Are you still working or planning to work during your early retirement years? If you start collecting benefits before reaching your full retirement age and continue to work, your benefits might be subject to an earnings limit, resulting in a reduction of your Social Security payments.
Spousal Benefits: If you are married, consider your spouse’s Social Security benefits as well. Certain strategies can allow spouses to claim benefits based on each other’s records, providing potential advantages and increasing the overall household income.
Lifestyle and Personal Goals: Your lifestyle choices and personal goals also play a role in deciding when to start collecting benefits. If you dream of traveling, pursuing hobbies, or indulging in other retirement activities, a higher monthly benefit might enable you to achieve those goals.
Tax Implications: Keep in mind that Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income taxes depending on your total income and filing status. If you start collecting benefits early while still earning significant income, a portion of your benefits could be taxed. However, waiting to collect benefits might reduce your taxable income during your early retirement years.
Marital Status: If you are divorced but were married for at least ten years and have not remarried, you may be eligible to claim benefits based on your ex-spouse’s work record. Understanding the rules for spousal benefits can help you optimize your overall Social Security strategy.
Survivor Benefits: If you are the higher-earning spouse in a married couple and expect your spouse to outlive you, delaying benefits can be a way to increase the survivor benefit available to your spouse after your passing.
Social Security Solvency: The future solvency of the Social Security program is a topic of concern for many people. While the program is projected to be able to pay a significant portion of promised benefits even if changes aren’t made, the timing of your claim could influence how much you might receive in various scenarios. Staying informed about Social Security reforms and policy changes can be helpful when making your decision.
Strategies for Maximizing Benefits:
Delayed Retirement Credits: As mentioned earlier, delaying Social Security benefits beyond your full retirement age can result in a higher monthly payment. If possible, consider waiting until age 70 to initially claim your benefits to receive the maximum amount.
Suspending Your Retirement Benefits: If you have reached full retirement age, but are not yet age 70, you can ask the Social Security Administration to suspend your retirement benefit payments. By doing this, you will earn delayed retirement credits for each month your benefits are suspended, which will result in a higher benefit payment to you. If your benefit payments are suspended, they will automatically start again the month you reach age 70. If you voluntarily suspend your retirement benefit and you have others who receive benefits on your record, they will not be able to receive benefits for the same period that your benefits are suspended.
Claim and Invest: If you start receiving benefits early and invest the money wisely, you may generate higher returns that can compensate for the reduced Social Security benefits over time.
Conclusion:
Choosing when to start collecting Social Security retirement benefits is a multi-faceted decision that requires a careful assessment of your individual circumstances, financial goals, and health considerations. There is no one-size-fits-all answer, and it’s crucial to take the time to evaluate all relevant factors. Seeking guidance from a JFS Wealth Advisor can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific situation, enabling you to make an informed choice that aligns with your long-term financial security and retirement aspirations. Ultimately, the key is to strike a balance between current financial needs and maximizing your benefits for a comfortable and fulfilling retirement.